Docker Image:
A Docker image is a lightweight, standalone, executable package that includes everything needed to run a piece of software, including the code, runtime, libraries, environment variables, and system tools.
Docker images are created by defining a set of instructions in a Dockerfile, which is essentially a script that specifies the dependencies and configuration needed for the software to run correctly. Once a Dockerfile is defined, it can be used to build an image, which can then be run as a container.

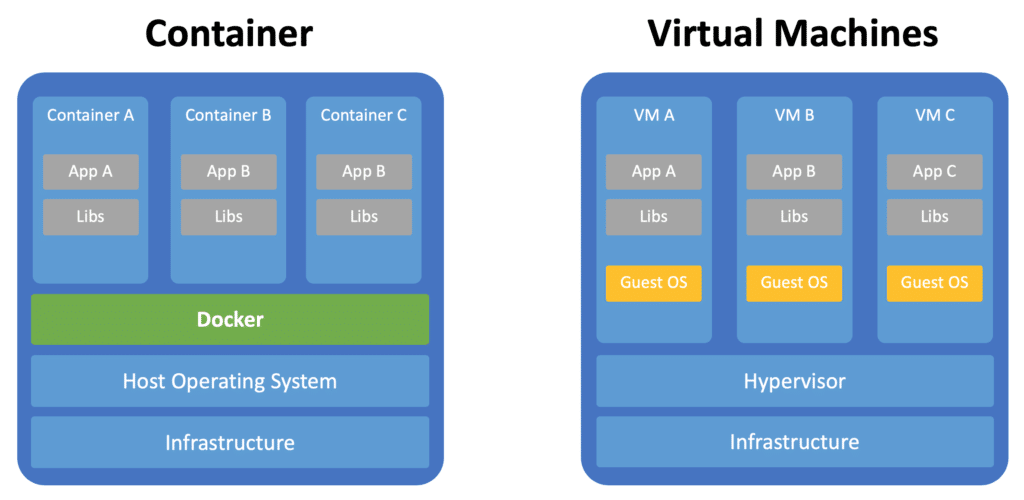
Containers
These are isolated environments containing their processes, networks and mounts.
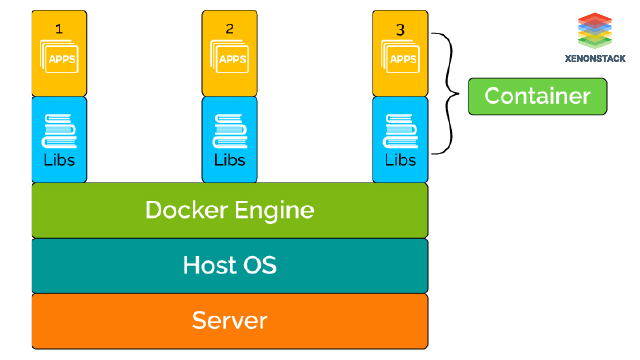
Docker
Docker is used to containerising applications that can run anywhere, anytime and as many times as you want in any environment.
Dockers can run on any flavour of OS on it as long as they have the same kernel.
Docker architecture

Docker Client
The Docker client uses commands to communicate with the Docker Daemon (Server). When a client runs any docker command on the docker client terminal, the client terminal sends these docker commands to the Docker daemon.
Docker Client uses Command Line Interface (CLI) to run the following commands
docker pull
docker build
docker run
Docker Host
Docker Host is used to providing an environment to execute and run applications. It contains the docker daemon, images, containers, networks, and storage.
Docker Registry
Docker Registry manages and stores the Docker images.
There are two types of registries in Docker -
Pubic Registry - Public Registry is also called a Docker hub.
Private Registry - It is used to share images within the enterprise.
Tasks
Use the
docker runcommand to start a new container and interact with it through the command line. [Hint: docker run hello-world]
Use the
docker inspectcommand to view detailed information about a container or image.

Use the docker port command to list the port mappings for a container.

Use the docker stats command to view resource usage statistics for one or more containers.
sudo docker stats -a

Use the docker top command to view the processes running inside a container.

Use the docker save command to save an image to a tar archive.

Thank you for reading my article.
Have a nice day.
